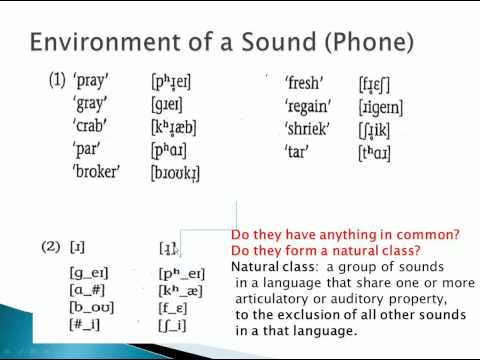
Hi, welcome to Introduction to Linguistics. Today, we are going to learn how to solve phonology problems. But before we do that, let's review some key concepts. First, what is a phoneme? A phoneme is a contrastive segment, minimal contrastive units of sounds. Phonemes are abstract mental entities that native speakers subconsciously understand. These sounds serve to distinguish the meaning of words in their language from one another. For example, when you have the sound of "t" in "time," you know that sound is different from the sound of "d" in "dime." So, we can say that although they have the same environment, these two sounds are different and are two different phonemes. Now, let's remember what an allophone is. An allophone is a distinct variant of a phoneme. It's the actual phonetic segment produced by a speaker. For example, when we have the phoneme "t," we don't always pronounce it the same way. We have variants like the aspirated "t" in "top," the unaspirated "t" in "stop," the flap "t" in "little," the glottal stop "t" in "kitten," and the syllabic "t" in "hunter" for some speakers. These are all variants of the same phoneme, "t." So, when you think about allophones, you remember they're non-contrastive. Now, let's see how to identify phonemes in a language. Phonemes make distinctions in meaning. If two sounds are members of separate phonemes, minimal pairs can almost always be found. Let's see an example of a minimal pair. A good example is "time" and "dime." This is a minimal pair because they have the same exact environment, and the only difference is one sound, which changes the meaning as well. The allophones of a phoneme are not a random collection of sounds but are a set of sounds that have the same psychological...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Why Form 5495 Underlying